DENTAL HEALTH
Bleeding gums – Warning sign and treatment
Bleeding gums – a serious warning signal from your body
Does biting an apple leave red marks? Does the toothpaste you spit out after brushing your teeth contain blood? Or do you have a metallic taste in your mouth? All of the above may indicate gingivitis, which is an acute inflammation of your gums, also known as gums. Here, you will learn why it is important to treat bleeding gums.
Bleeding gums are a serious warning signal from your body. It indicates inflammation of the entire periodontium, which professionals call periodontitis. This is a serious disease that, in the worst case scenario, will not only lead to tooth loss, but can also cause cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis or Alzheimer's.
Superficial inflamed gums (gingivitis) represent a preliminary stage, which can also manifest through bleeding gums. If you regularly notice bleeding gums, a visit to your dentist is essential.
Causes: Why do gums bleed?
As with any inflammation, your body will try to take action on its own. By increasing blood flow to the affected area, it tries to wash away the bacteria.
Symptoms of gingivitis:
Redness, swelling and pain. The gums will also swell, may take on a reddish color due to dilation of blood vessels, and react sensitively when you brush your teeth or bite into food.
Possible causes of bleeding gums include:
- Hormonal changes (pregnancy)
- Bacteria or poor oral hygiene
- Mechanical stresses (caused by protruding edges of fillings)
- Vitamin C deficiency or chemical processes.
Our product recommendations
1. The most common cause of bleeding gums and periodontitis: lack of oral hygiene
Irregular tooth brushing and poor oral hygiene are the most common causes of bleeding from the gums, i.e. the gums. Within a short time after eating, a thin layer of plaque forms on the teeth. If the teeth are not cleaned regularly enough, this layer thickens. Finally, the plaque manifests itself in a solid form as stone, which offers particularly good conditions for the bacteria found in the plaque. Over time, these bacteria can spread to your gums and periodontium. Then gingivitis (inflammation of the gums) and periodontitis (inflammation of the periodontium) develop.
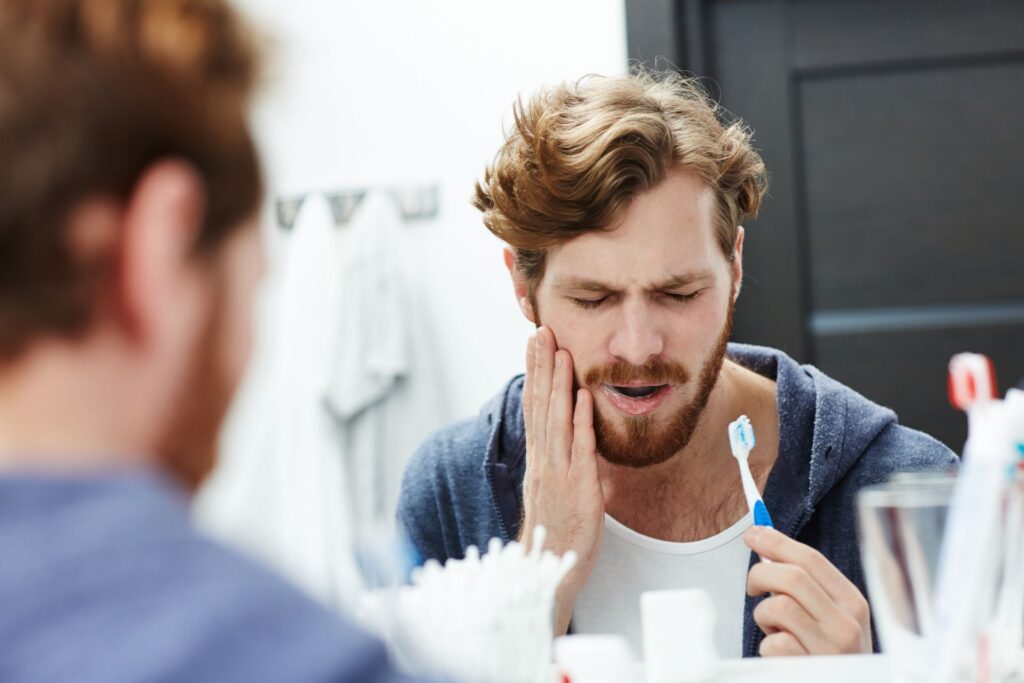

2. Bleeding gums due to hormonal changes during pregnancy

Compared to non-pregnant women, proper cleaning technique and thorough oral hygiene are even more important for pregnant and lactating women. As this is the only way to actively prevent gingivitis or periodontitis caused by pregnancy.
The hormonal changes that take place in the body during pregnancy mean that your body reacts more easily to bacterial plaque. Plaque causes irritation faster and makes gums bleed faster. This can be prevented by professional teeth cleaning, dental check-ups in early pregnancy and good oral hygiene.
3. Bleeding gums due to inadequate sealing margins and dentures
Fillings that protrude beyond the tooth boundaries and into the interdental spaces create a breeding ground for bacteria. This often happens with old amalgam fillings. A permanent colonization with harmful bacteria leads to gingivitis. Even thorough tooth brushing often does not help here – the bristles of the toothbrush cannot reach these niches. Bleeding begins.
Unlike bleeding gums caused by poor oral hygiene, in this case the gums bleed at specific points, i.e. directly at the sealing site. As a result of this microbial load, the gums often recede, which leads to receding gums and gum pockets. Your dentist checks the edges of the newly placed fillings using a probe or dental floss and thus checks the accessibility of the interdental space.
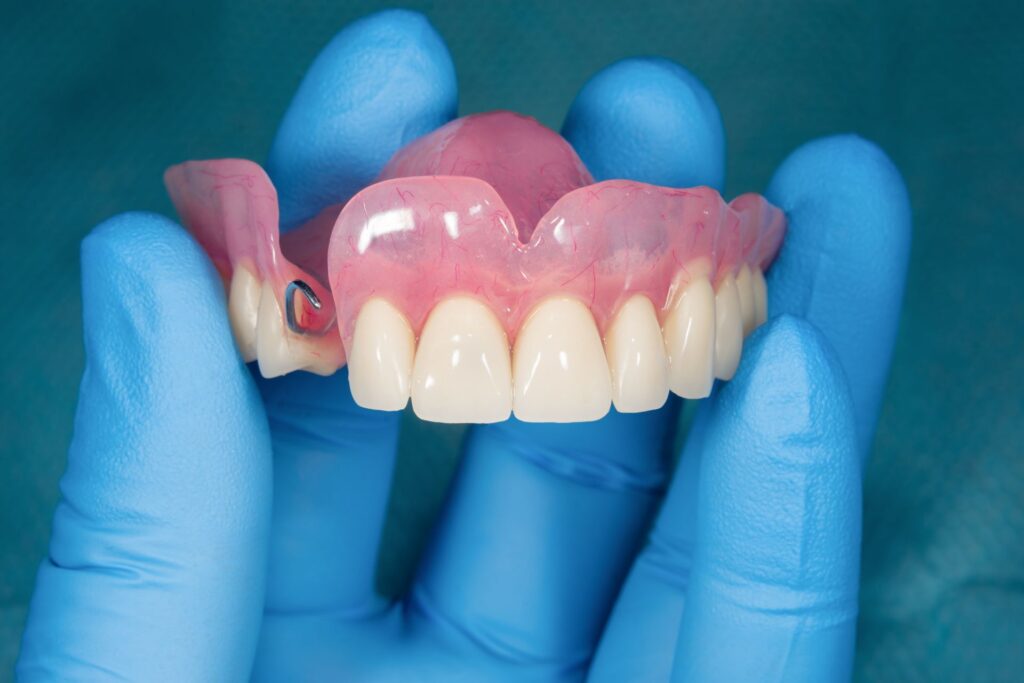
The same applies to removable dentures: excessive pressure loads irritate the gums (gums) and inflammation occurs, which is painful and not always easily corrected. Without dentures, patients often do not feel comfortable speaking. If the denture cannot be worn due to pressure inflammation, it is difficult to eat. Many patients tend to wear their dentures eventually. It is important to break this vicious cycle and eliminate the pressure points on the dentures. This often requires only a minor adjustment to the denture, which allows the gums to heal and stop bleeding.
First steps: How to protect yourself from bleeding gums
- Regular brushing and proper dental care
- Regular checkups with your dentist
- Professional teeth cleaning once or twice a year
- Avoiding risk factors such as smoking
The LACALUT® effect: Medical triple protection
- Reduces the sensitivity of teeth to pain
- Prevents gum disease
- Hardens tooth enamel
1. Regular tooth brushing
Regular checkups with your dentist are among the most important preventive measures against periodontitis. Professional teeth cleaning is recommended once or twice a year.
Tip: Many insurance companies also offer comprehensive worry-free dental protection, which takes care of having your teeth professionally cleaned so you can continue to stand out with a beautiful smile in the future. Patients often notice inadequate fillings when food debris gets stuck between the teeth. Don't forget to mention this to your dentist at one of your check-ups.

2. Regular check-ups and professional teeth cleaning at the dental office

Regular checkups at your dental office are among the most important preventive measures against periodontitis. Professional teeth cleaning is recommended once or twice a year.
Tip: All-round carefree dental care from dentolo also takes care of professional cleaning of your teeth, so you can continue to stand out with a beautiful smile in the future. Patients often notice inadequate fillings when food debris gets stuck between the teeth. Don't forget to mention this to your dentist at one of your check-ups.
3. Avoid risk factors
Smoking constricts your blood vessels, which also changes blood flow to the gums. In addition, it reduces the immune system. Bleeding gums are closely related to smoking.
Protect yourself effectively from heart disease with healthy gums. Inside the mouth, there is a constant interplay between bacterial defenses and bacterial proliferation. As a whole it is called oral flora.
If the growth of bacteria gets the upper hand due to poor oral hygiene, various diseases develop in the mouth. The best known are probably tooth decay and inflammation of the gums (periodontitis). However, heart inflammation can also be caused by poor oral hygiene.

Streptococci, spherical bacteria, are part of a healthy oral flora. However, there are some subforms that can multiply well in the plaque and which are also known to cause inflammation of the heart. These are called Streptococcus mutans. In this case, they are especially likely to attack the inner lining of the heart muscle, also known as the endocardium. This leads to endocarditis. The risk of heart attack increases. This is why it is important not to let tooth decay develop or to have it treated quickly by a dentist.



